[pac_divi_table_of_contents included_headings="on|on|on|off|off|off" minimum_number_of_headings="6" scroll_speed="8500ms" level_markers_1="decimal" level_markers_3="none" title_container_bg_color="#004274" admin_label="Table Of Contents Maker"...

Enhancing Customer Engagement with Data Management Platforms and Omni-Channel Strategies
Businesses must adapt to the fast-paced digital environment by employing advanced technologies. Data Management Platforms (DMPs) and Omni-Channel strategies have developed into strong tools for boosting customer engagement, fortifying marketing endeavors as well as propelling business expansion. This article will concentrate on intricacies of DMPs and Omni-Channel strategies, their advantages and how they can be successfully fused for maximum business potential.
Understanding Data Management Platforms (DMPs)
Definition and Importance of the DMPs
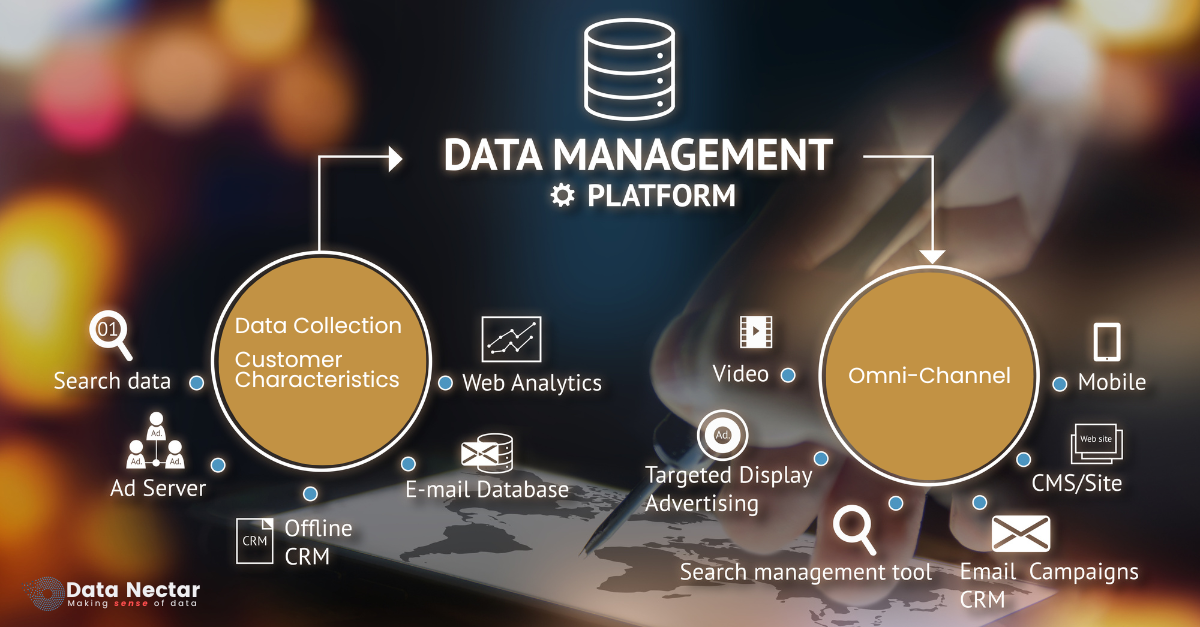
A Data Management Platform (DMP) is an integrated system that collates, arranges and actuates a huge amount of data from different sources. It plays an essential role in managing user information, monitoring customer behaviour and optimizing marketing campaigns. Through data consolidation, DMPs enable firms to develop exhaustive client profiles hence deliver personalized experiences.
Key Components of DMPs
- Data Collection: Search data, customer attributes among other details are collected by DMPs from various places such as web analytics, CRM systems, ad servers plus email databases.
- Data Integration: The platform unites information received via varied channels so that there is a single representation of interactions between customers.
- Segmentation: DMPs categorise data into segments based on predefined criteria, allowing businesses to target specific customer groups.
- Activation: Using the segmented data, DMPs enable targeted advertising, personalized content delivery, and efficient marketing campaigns.
The Role of Omni-Channel Strategies
Definition and Benefits
Omni-Channel strategies involve providing a seamless and integrated customer experience across various channels, including online and offline platforms. This approach ensures consistent messaging and interaction, regardless of the channel used by the customer.
Benefits of Omni-Channel Strategies:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Customers enjoy a cohesive experience, whether they are interacting via mobile, web, email, or in-store.
- Increased Engagement: Consistent communication across channels leads to higher customer engagement and loyalty.
- Better Insights: Businesses can gather comprehensive data on customer behaviour across all touchpoints, enabling more informed decision-making.
Integrating Omni-Channel with DMPs
Combining DMPs with Omni-Channel strategies allows businesses to leverage data more effectively. By integrating data from various channels, companies can create unified customer profiles and deliver personalized experiences across all touchpoints. This integration facilitates better targeting, improved customer retention, and higher conversion rates.
Enhancing Data Collection and Customer Insights
Sources of Data Collection
DMPs collect data from a variety of sources, including:
- Search Data: Information about what customers are searching for online.
- Web Analytics: Insights into website traffic, user behaviour, and conversion rates.
- Ad Servers: Data on ad impressions, clicks, and conversions.
- Email Databases: Information from email marketing campaigns.
- Offline CRM Data: Customer information collected from offline interactions and CRM systems.
Leveraging Customer Characteristics
By analyzing customer characteristics, businesses can gain valuable insights into their preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns. This information enables companies to create targeted marketing campaigns, offer personalized recommendations, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
Driving Marketing Success with Targeted Advertising
1) Targeted Display Advertising
Targeted display advertising involves using data to deliver ads to specific customer segments. By leveraging DMPs, businesses can identify the most relevant audiences and create tailored ad campaigns that resonate with their interests and needs. This approach increases the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
2) Using Web Analytics for Better Campaigns
Web analytics provide critical insights into the performance of marketing campaigns. By analyzing metrics such as click-through rates, conversion rates, and user behaviour, businesses can refine their strategies, optimize ad placements, and improve overall campaign effectiveness.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Many businesses have successfully implemented DMPs and Omni-Channel strategies to achieve significant results. For instance, a retail company used a DMP to consolidate customer data from online and offline sources, enabling them to deliver personalized marketing messages and increase sales. Similarly, a financial services firm integrated their DMP with an Omni-Channel strategy, resulting in higher customer engagement and improved retention rates.
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, leveraging Data Management Platforms and Omni-Channel strategies is essential for business success. By effectively collecting, integrating, and activating data, businesses can enhance customer experiences, drive targeted marketing campaigns, and achieve better business outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, companies that invest in these tools will be well-positioned to stay ahead of the competition.
Ready to take your business to the next level with advanced data management and marketing strategies? Contact Data Nectar today to learn how our Data Management Platform and Omni-Channel solutions can help you achieve your goals. Let us assist you in making sense of data and driving your business forward.
Enhance Customer Engagement
Ready to transform your customer engagement? Get started with our data management and omni-channel strategies today!
Recent Post
Top Benefits of Data Governance for Your Organization
Enhancing Customer Engagement with Data Management Platforms and Omni-Channel Strategies
[pac_divi_table_of_contents included_headings="on|on|on|off|off|off" minimum_number_of_headings="6" scroll_speed="8500ms" level_markers_1="decimal" level_markers_3="none" title_container_bg_color="#004274" admin_label="Table Of Contents Maker"...
AI Personalization Excellence: Enhancing Customer Engagement in 2024
[pac_divi_table_of_contents included_headings="off|on|on|off|off|off" scroll_speed="8500ms" level_markers_3="none" title_container_bg_color="#004274" _builder_version="4.22.2" _module_preset="default" vertical_offset_tablet="0" horizontal_offset_tablet="0"...